For straps, holdowns and other structural connectors, the first step is to identify the product that meets the load and corrosion-resistance requirements for your project. The next step is to determine the appropriate fasteners. The Wood Construction Connectors catalog, C-C-2017, offers fastener information for every Simpson Strong-Tie connector used in wood construction. Many of our connectors are designed to be installed with connector nails, Strong-Drive® SD Connector screws or Strong-Drive SDS Heavy-Duty Connector screws. If you properly determine the type and number of fasteners needed for your job and install them correctly, as shown in the catalog, then your installation will meet the full load-capacity values.
Figure 1 is a snippet from page 76 of catalog C-C-2017. The face-mount hanger table gives the size and number of nails to be installed in the header and the joist, and the table note defines the nail-size terminology. Let’s take a look at the various fasteners used with Simpson Strong-Tie connectors.
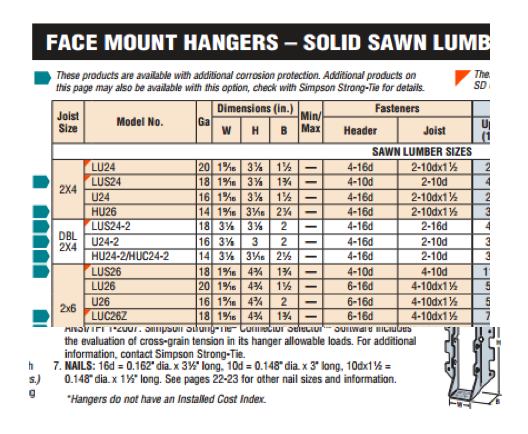
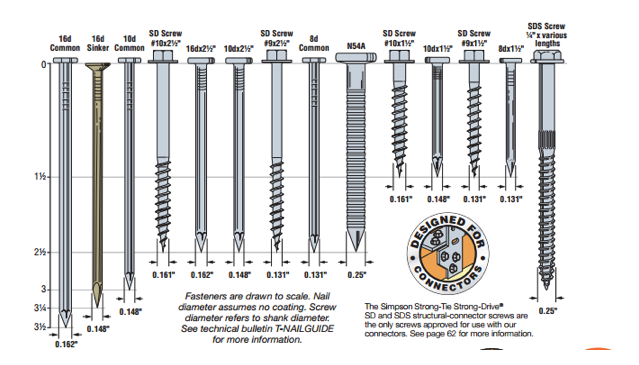
Figure 2 shows a scale view of almost all the fasteners used with our connectors. You can find this illustration in the Fastening Systems catalog (which also comes in a job site friendly pocket size), C-F-2017, and the Wood Construction Connectors catalog, C-C-2017. However, we are continually designing, evaluating and adding new fasteners to use with our connectors. Check our website for the latest product offering.
For every connector and fastener combination, there are a few things to keep in mind.
- Type and size — Be sure to determine the correct type and size of fastener; for nails, size means diameter and length.
- Do not mix fasteners — Do not combine nails and screws in the same connector unless the load table specifically allows it.
- Corrosion resistance — Consider environmental corrosion and galvanic corrosion. For environmental corrosion, select fasteners that have corrosion resistance similar to that of the connector; for galvanic corrosion, the fasteners and connector should be galvanically compatible (e.g., pair stainless-steel fasteners with stainless-steel connectors, hot-dip galvanized fasteners with hot-dip galvanized or ZMAX® connectors). Figure 3 shows the corrosion resistance recommendations for fasteners and connectors.
Strong-Drive® Nails
There are two types of connector nails available, the Strong-Drive SCNR Ring-Shank Connector nail and the Strong-Drive SCN Smooth-Shank Connector nail. “SCN” stands for Structural Connector Nails. “R” refers to ring-shank nails. Currently all our ring-shank connector nails are available in Type 316 stainless steel. Stainless-steel ring-shank nails are recommended for stainless-steel connectors.
Simpson Strong-Tie connector nail specifications include common nails, sinker nails and short nails. Nails can be driven with a hammer or with a power tool.
Strong-Drive® SD Connector Screws
There are approximately 150 Simpson Strong-Tie connectors that can be installed with Simpson Strong-Tie Strong-Drive SD Connector screws. The shanks of the SD Connector screws are designed to match the fastener holes in Simpson Strong-Tie connectors. SD screws can make connector and strap installation easier and can also provide some resistance beyond what nails may offer. Ease of installation is sometimes critical when you’re working in tight spaces where a screw-driving tool may maneuver better than a hammer or a power nailer. Some installations also will be made more secure if you use screws instead of nails, especially in applications where fastener pullout is a possibility. For example, joist hangers in a deck can pull away from the deck ledger unless the fasteners provide appropriate withdrawal resistance.
Here are a few selection and construction tips for SD screws:
- SD10 screws replace 16d common and N16 nails in face-mount hangers and straps.
- SD9 screws replace 8d and 10d common and 1-1/2″ size nails and 16d sinker nails (all nails 0.148″ and 0.131″ diameter) in face-mount hangers and straps.
- When using SD screws as double-shear fasteners, the 2 1/2″ SD screws are the correct length.
- When SD screws are to be used as an alternative to nails, select and use only SD screws. Other types of screws should not be substituted.
- SD screws are required to be installed by turning. Do not drive them with a hammer or palm nailer.
- SD screws and nails cannot be mixed in the same connector.
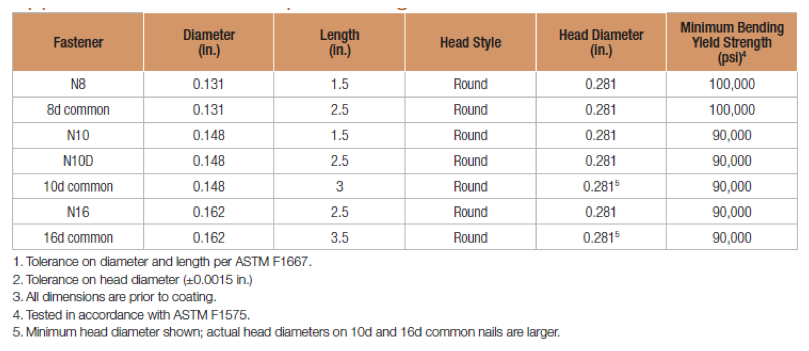
Strong Drive® SDS Heavy-Duty Connector Screws
The Simpson Strong-Tie Strong-Drive SDS Heavy-Duty Connector screws are 1/4″ screws with a hex-washer head. They’re available in nine lengths. SDS screws are available with a double-barrier coating or in Type 316 stainless steel. These screws can be installed without predrilling and have been extensively tested in various applications. SDS screws can be used for both interior and exterior applications, including in chemically treated wood.
Three Important Considerations for Successful Connector Fastening
When starting your next project, remembering these three things will put you on the path to success:
- Enhance durability by selecting fasteners and connectors suited to the environmental and material conditions and that are compatible with each other galvanically and in their corrosion resistance.
- Maximize capacity by selecting the appropriate type and size of fasteners for the connector.
- Optimize performance by using Strong-Drive fasteners and by not mixing nails and screws in the same connector.
Simpson Strong-Tie® Composite Strengthening Systems™
For more information about the nails and screws recommended for use with Simpson Strong-Tie connectors, visitstrongtie.com and see the appropriate product page or view our catalogs.
Let us know what additional questions you have about using Simpson Strong-Tie fasteners with Simpson Strong-Tie connectors.